SMU Graduate Learning Outcomes (GLOs)
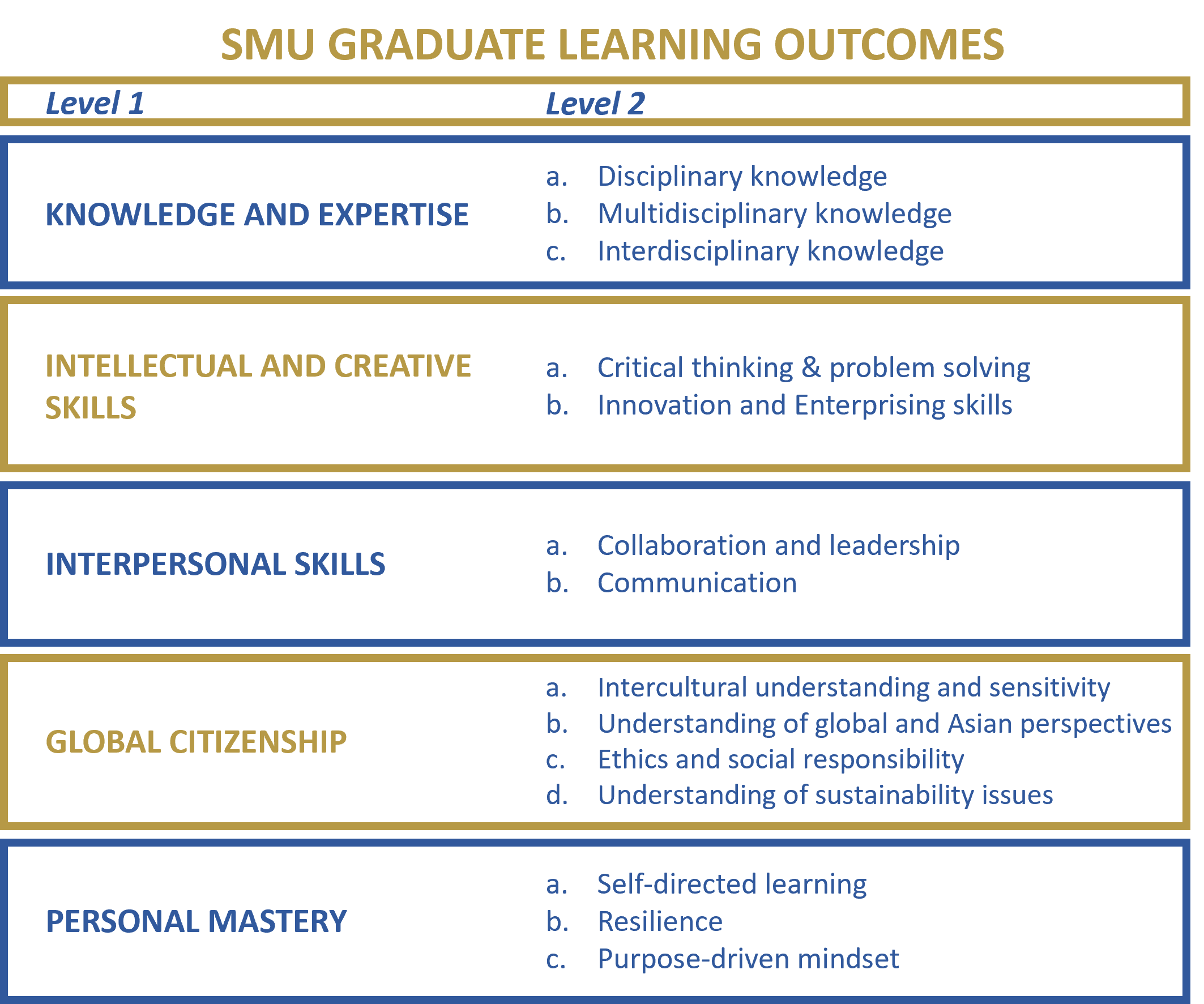
In 2017, SMU’s Blue Ribbon Commission for Undergraduate Education (BRC-UG) established a set of SMU Graduate Learning Outcomes (GLOs) - learning goals that are important to all undergraduates regardless of their discipline. These are:
- Knowledge and expertise
- Intellectual and creative skills
- Interpersonal skills
- Global citizenship
- Personal mastery
In short, SMU seeks to develop broadly educated individuals, with depth of knowledge in selected domains, and workplace capabilities required to thrive in the 21st century.
These GLOs provide a meta-level for the entire SMU undergraduate experience, delivered through the holistic SMU undergraduate education comprising the Core Curriculum, disciplinary curriculum and co-curriculum components. Collectively, these three components will deliver the full set of the SMU GLOs.
The SMU Pedagogy
The BRC-UG recognises that effective delivery of the SMU GLOs is dependent on the University’s distinctive pedagogies – personalised learning; collaborative and interactive learning; and experiential learning. Underpinning these three key pedagogical approaches is technology enhanced learning, where technology will enhance personalisation, interaction and collaboration, and experience of the real world.
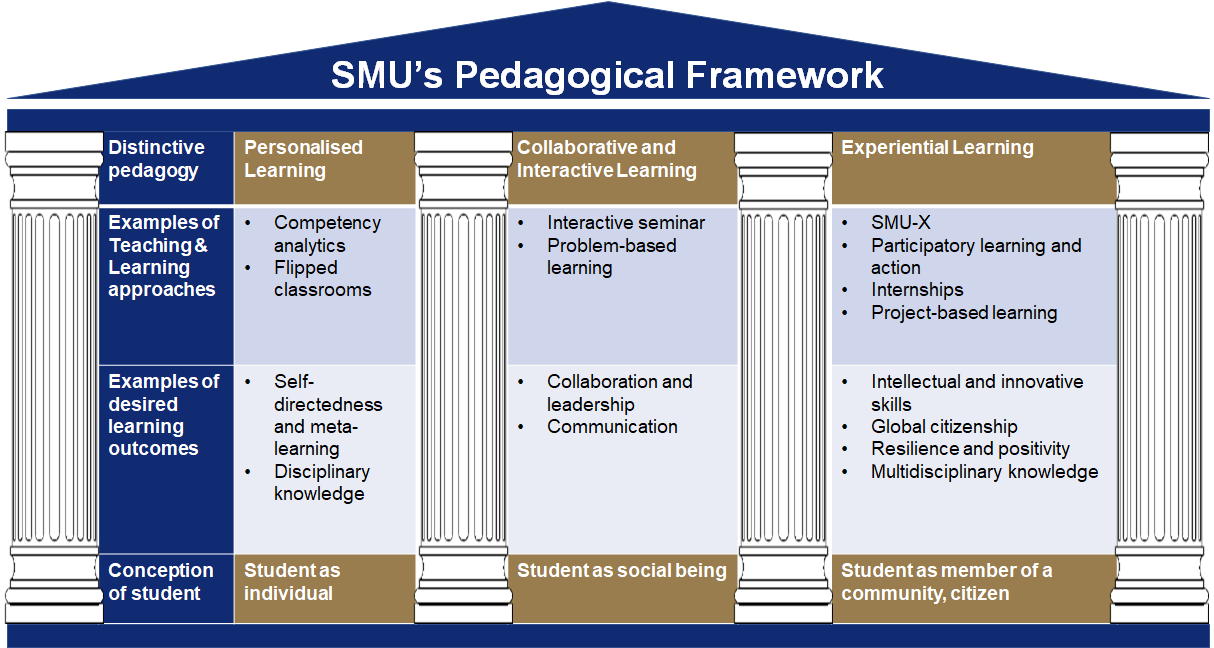
- Student as an individual:
Student learning is facilitated and enhanced through personalised learning. Teaching and learning approaches used should recognise individual differences across students in terms of their learning needs, learning preferences, interests and progress, and allow for greater individualised attention, for example through the use of adaptive digital learning tools, and flipped classrooms. - Student as a social being:
Student learning is facilitated and enhanced through collaborative and interactive learning. Teaching and learning approaches should allow students to interact, discuss and debate with others, and include interactive seminars, and problem-based learning. - Student as a member of a community and as a citizen:
Student learning is facilitated and enhanced through experiential learning. Teaching and learning approaches should empower students’ contributions to their community and include SMU-X, participatory learning and action, internships, and project-based learning.
Each of the distinctive pedagogies is student-centered and when implemented effectively, will help to deliver SMU’s Graduate Learning Outcomes.
Bibliography
- Mayes, T., & De Freitas, S. (2004). Review of e-learning theories, frameworks and models.
- Singapore Management University (2018). SMU Blue Ribbon Commission on Undergraduate Education Report.