Suggested Practices for Teaching with Generative AI Tools
Teach students how to use Generative AI Tools well
-
Clearly communicate expectations and guidelines for using generative AI tools to students. This could include pointers such as the types of tasks the generative AI tool is appropriate for, what the limitations of the tool are, and how the AI-generated responses will be used to help student learning.
-
Ensure that the use of generative AI tools aligns with your overall assessment and learning goals. The use of AI tools should enhance assessment and learning experience, not detract from it.
-
Provide students with opportunities to reflect on their use of generative AI tools and how it relates to their learning. This could include prompts for self-reflection or small-group discussions.
-
Encouraging self-directed learning by allowing students to generate answers to questions they may have and verify the appropriateness of the answers through further research.
-
If appropriate, provide students with opportunities to learn about AI technology and how it works. This will help increase their awareness and appreciation of how AI is likely to shape the world of work they will be joining soon.
Use Generative AI Tools to improve your productivity as an instructor
-
Use it as a tool to assist you in creating educational content, such as writing practice exercises, creating interactive lessons, or creating rubrics for assessments you have created.
-
Use it to seek ideas for assessment questions formulation.
Using Generative AI Chatbots to Seek Ideas for Assessment Questions
In recent years, generative AI technologies have revolutionised various aspects of education and assessment. Among these advancements, the use of generative AI chatbots for formulating assessment questions has emerged as a promising tool to streamline the question creation process, enhance engagement, and improve the quality of assessments. By leveraging the capabilities of these AI-powered conversational agents, educators and content creators can efficiently generate diverse and tailored sets of assessment questions across different subjects and levels of complexity.
This section provides pointers and suggestions for instructors who are keen to explore how Generative AI chatbots can assist in the formulation of assessment questions.
It is important to note upfront, that regardless of which tools are used, instructors remain responsible for ensuring assessments are constructively aligned, valid, reliable, fair, and in line with SMU assessment policy. For details on the SMU assessment policy, please click HERE.
Note also that, while this document focuses on Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) and Essay questions for Final Exams, instructors could also apply these pointers and suggestions to other assessments.
Generative AI chatbots are at their most helpful when users can clearly define and articulate their objectives and the relevant context and factors. Hence, it is important that instructors exercise their due diligence in planning and clarifying key information such as the learning objectives, assessment type, degree of difficulty for students that are aligned to course requirements. For more information on assessment planning and design, please refer to our page on setting quizzes and exams.
- Define Learning objectives
Lock in the specific knowledge and skills you want to assess. This will guide you in crafting prompts for Generative AI chatbots. Consider using verbs from the Blooms' Revised Taxonomy to help state what students are to demonstrate.
- Prepare your training materials
Feed the chatbot relevant course materials like lectures, notes, textbooks, and past exams. If your course refers to important and well-known works and concepts, specifying these would suffice without needing to insert the entire source. The more relevant data you provide, the better Generative AI chatbots can tailor questions to your needs.
- Specify types of Assessment Questions
Provide inputs on the types of Assessment questions like MCQ, short answer questions, essays, etc. This helps tailor the output to your assessment format. You could even set the difficulty level by specifying whether you want easy, medium, or challenging questions.
Do ensure your inputs and generated outputs are in line with SMU assessment policy (Click HERE for details)
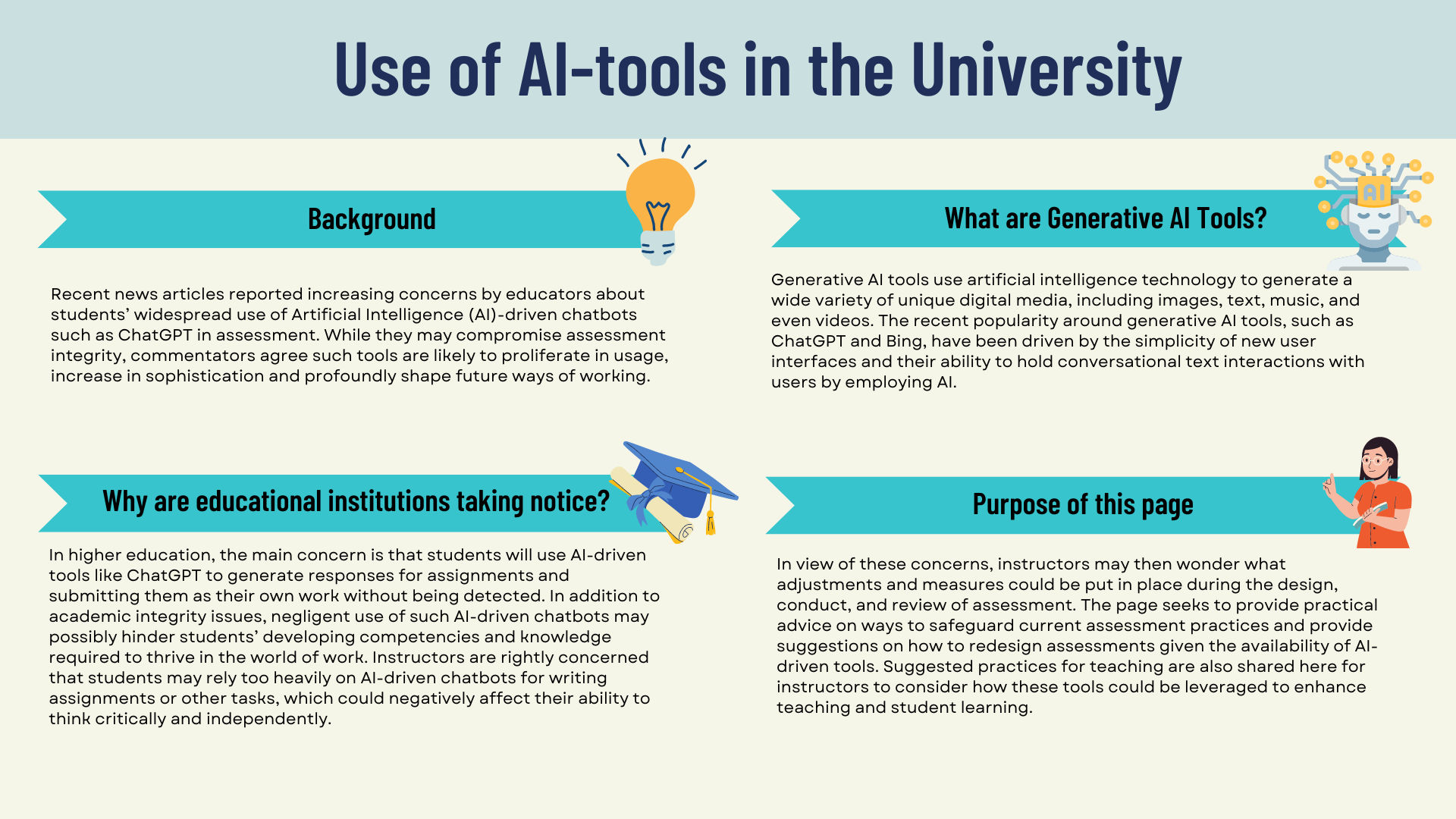
As Generative AI technologies continue to evolve and grow in sophistication, more and more new chatbots are now available. Here's a selection of some of the better known (points below apply to the free tier):
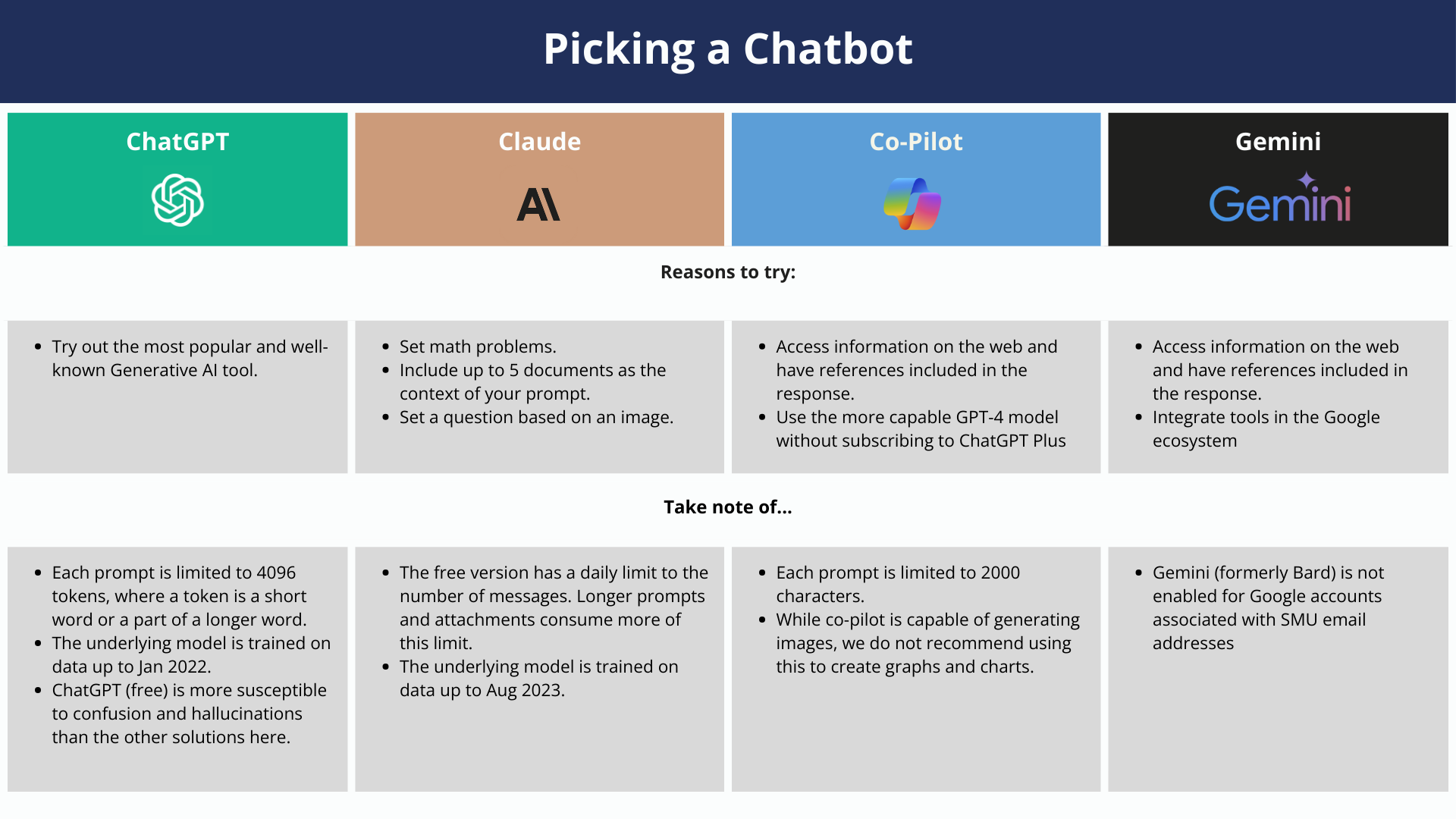
For more information on the performance benchmarks of the most popular Large Language Models (LLMs), please refer to the reports published by Anthropic or Vellum.
Success in using Generative AI chatbots is determined to a significant degree by the quality of the prompt provided. Here are some guidelines to create better prompts:
- When choosing the model to work with, the latest and most capable models are likely to perform better.
- Start with a simple and short prompt, and iterate from there.
- Put the instructions at the beginning of the prompt, or at the very end. When working with large context, models apply various optimizations to prevent Attention complexity from scaling quadratically. This may make a model more attentive to the beginning or end of a prompt than the middle.
- Clearly separate instructions from the text they apply to - more on this in the next section.
- Be specific and descriptive about the task and the desired outcome - its format, length, style, language, etc.
- Avoid ambiguous descriptions and instructions.
- Favor instructions that say “what to do” instead of those that say “what not to do”.
- “Lead” the output in the right direction by writing the first word (or even begin the first sentence for the model).
- Use advanced techniques like Few-shot prompting and Chain-of-thought
- Test your prompts with different models to assess their robustness.
- Version and track the performance of your prompts.
When using generative AI chatbots, exercise care in checking and using the outputs, as responses from chatbots such as ChatGPT can contain inaccuracies, made-up sources and content, and offensive material.
Do also note that copyright principles and intellectual property rights apply in what you feed generative AI chatbots. Possible infringements include the feeding of copyrighted materials such as textbooks, articles, pictures, etc. For copyright concerns and advisory, please seek SMU Libraries support by clicking HERE.
For certain types of questions, the suggested approach may not work as well. These include questions that involve:
- Mathematical problems
- Coding problems
- Complex reasoning tasks
- Highly specialised / obscure areas of knowledge
Generative AI chatbots can be powerful tools for generating diverse and thought-provoking assessment questions, but human oversight and guidance are still essential for ensuring the questions are tailored to your specific learning objectives.
The following are some tips that may be helpful in refining and checking the outputs:
- Request for and check that the sources provided are real. Generative AI chatbots with internet access, such as Co-Pilot and Gemini, are able to check the responses given with a web search.
- Follow up on a question to be refined by requesting for multiple versions of it, specifying the aspects of it to vary if possible.
- Iterate on smaller subsets of questions, or even single questions. This is likely to produce better results than trying to improve everything simultaneously.
- Input questions you have used for an exam before and ask the tool to generate a different question.
Generative AI chatbots can be powerful tools for generating diverse and thought-provoking assessment questions, but human oversight and guidance are still essential for ensuring the questions are tailored to your specific learning objectives.
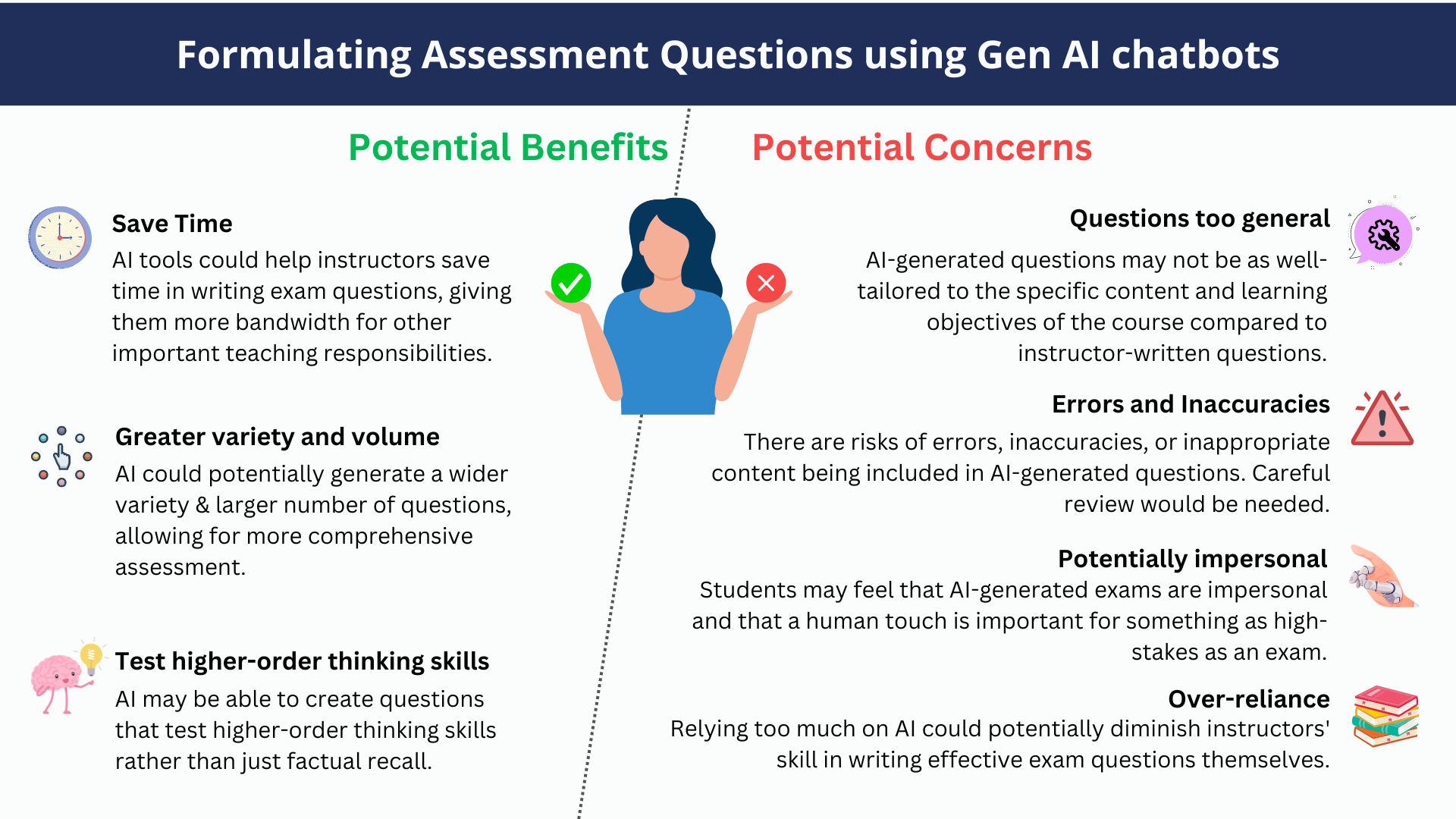
Overall, if AI tools are used carefully and questions are thoroughly reviewed, they could potentially be a helpful supplementary tool for busy professors. However, fully outsourcing exam creation to AI is risky. At most, AI should assist and inspire human question-writing, not replace it.
Human judgment, subject matter expertise, and understanding of the nuances of the course material should be central in the exam development process. Technology can assist, but should not be the sole author of something as important as exam questions.
SMU instructors may access this resource for additional tips and FAQs.
Suggested Practices to Safeguard Assessment Integrity
-
Clarify what is authorised and unauthorised use
-
Have open and transparent discussions with students regarding the acceptable and unacceptable use of AI in assessments. This should include explicit instructions and expectations of what constitutes appropriate use, such as the production of original work. For example, you could allow the use of AI tools, if its use is acknowledged and described, and the text is paraphrased. For some assignments you can specify that the use is not allowed.
-
Students should be informed that any unacceptable use of generative AI tools will be considered a violation of the SMU Code of Academic Integrity and will be dealt with accordingly.
-
-
Detect unauthorised use where possible
-
Use generative AI tools such as ChatGPT or Bing to see examples of the answers it can generate for your assignments. This can help you identify patterns in how the responses are framed.
-
Due to the nature of some generative AI tools' set up, there are signs you can pay attention to in order to make an initial judgement on whether a piece of writing is AI-generated. For example, you can look out for:
-
the absence of personal experiences or emotions
-
inconsistency in writing style compared with in-class assessments
-
lack of in-text citation or wrong citations
-
- You may explore AI-detection tools such as GPTZero and Originality.AI. Turnitin also recently introduced AI detection capabilities. It is worth noting these detection tools are work in progress and their results may be unreliable. More effort is also needed to put each student’s work through such scans before grading as automated ways of scanning batches of submissions are currently lacking.
-
For more information on AI-detection tools, please click HERE, or contact IITS elearn team at lms_support [at] smu.edu.sg.
-
In the event unauthorised use of AI tools is detected after applying detection tools, you may use the DRIVE approach to investigate further. Click HERE for details.
-
-
Shift emphasis to in-class assessments
-
Consider converting some take-home assignments to in-class assessments without access to the internet. This may require breaking up larger assignments into component pieces. It can be suitable when the targeted learning outcomes relate to critical thinking, problem-solving, or written communication based working knowledge of one or more disciplines. For example, as part of a larger group project, you can organize an individual in-class assessment in which students are required to write a 500-word draft of a certain section of the report.
-
-
Redesign assessments beyond capabilities of AI tools
-
If appropriate, complement and vary different forms of assessment. For example, following up a written assignment with an oral presentation.
- In assessment questions, include information that is not available on the internet and information that AI engines cannot gather. For example, use questions that require the use of include personal experience, cases/examples discussed in class.
- Include the use of reflective responses that build in personal insight. AI tools are far less useful in this context.
- If appropriate, incorporate diagrams, graphs or pictures as part of the assessment questions (eLearn quizzes can facilitate this).
- Introduce authentic assessment which involves tasks or activities that closely mirror real life challenges, requiring students to apply knowledge and skills in a practical or problem-solving context. For example, in certain law courses, students can be assessed using mock trials.
- Try your assignment in generative AI tools so that you can find out how it fails to do well and then add grading criteria that measure exactly those qualities (such as relevance to context, specificity, authenticity).
- Ask students to provide an annotated bibliography and describe how references were used in their assignment.
-
-
Integrate Generative AI Tools into assessments
-
Consider using the generative AI tools as a supplement to other forms of assessment. For example, ask students to critique or build on an AI generated response.
-
Tips for different assessment types
-
Focus on knowledge application instead of the final product. Ask for a clear demonstration of the application of core concepts and ideas to a specific audience, or context. Place this inside an authentic problem that requires critical appraisal of data and research (like a detailed case study). For example, rather than asking for a summary of research into a topic, ask students to write a proposal that shows the application of the outcomes of the research to resolve a specific problem. Follow this with required reflections from students detailing how they adapted the research findings from the general to the specific.
-
Focus on the process instead of the final product. For example, getting students to submit an outline and multiple drafts for an assignment and see how they develop their arguments. The meta-data for each draft should show their editing time, changes made, etc. If they lifted content from generative AI tools, the meta-data may show massive changes in a very short editing time.
-
Assessment question design. The assessment question could include information that is not available on the internet, and information that AI engines cannot gather. For example, questions or responses that include personal experience, cases/examples discussed in class. You may also consider getting students to critique draft responses generated by AI tools.
-
Complement and vary different types of assessment. For example, following up a written assignment with an oral presentation where clarifying questions can be asked
Content
- Focus the presentation on application of core concepts to an authentic context/problem. Students may be encouraged to relate concepts to local or personal experiences.
Delivery
- Allow significant time after the presentation for a detailed question and answer session to allow the students to demonstrate their understanding of the topic (rather than just their ability to read from a script).
- Change the grading structure to weigh the answers to the Q&A more heavily.
Where appropriate assume that the code has been AI generated, so ask the students to do either or both of the following:
- Answer detailed questions on the specific choices made (For example, why a particular field would be needed in a database).
- Find and fix broken code under exam conditions. Explain why it was broken and what they would do to fix it, and why their fix would work.
Ask for demonstration of understanding of the data rather than the ability to generate them. For example, ask students to determine whether they believe that there is likely to be fraudulent behavior in the company as a result of their analysis of the figures.
Consider making them closed-book and using eLearn quizzes with lock-down browser. If a degree of open book is needed, consider only allowing physical paper or books.
Related Resources
This article recommends alternative assessments, including inviting students to use chatbots to produce writing they can critique.
This article shares practical advice on ensuring academic integrity
The paper above contains useful recommendations to integrate ChatGPT into teaching.
A shared document constantly updated with AI-related resources – such as articles, journal papers, etc.
Here's an example of it in action using different types of assessment: Essay, Lit Review, Short Answer Questions, Generating Recommendations, Case Studies and Reflection Questions
Ending Notes
If you are keen to share your teaching or assessment practice on the use of ChatGPT, kindly contact cte [at] smu.edu.sg.
The information here is current as of Apr 2024. Due to the evolving nature of emerging technologies and their impact, we will be periodically updating this page with new information and tips, so do check back.